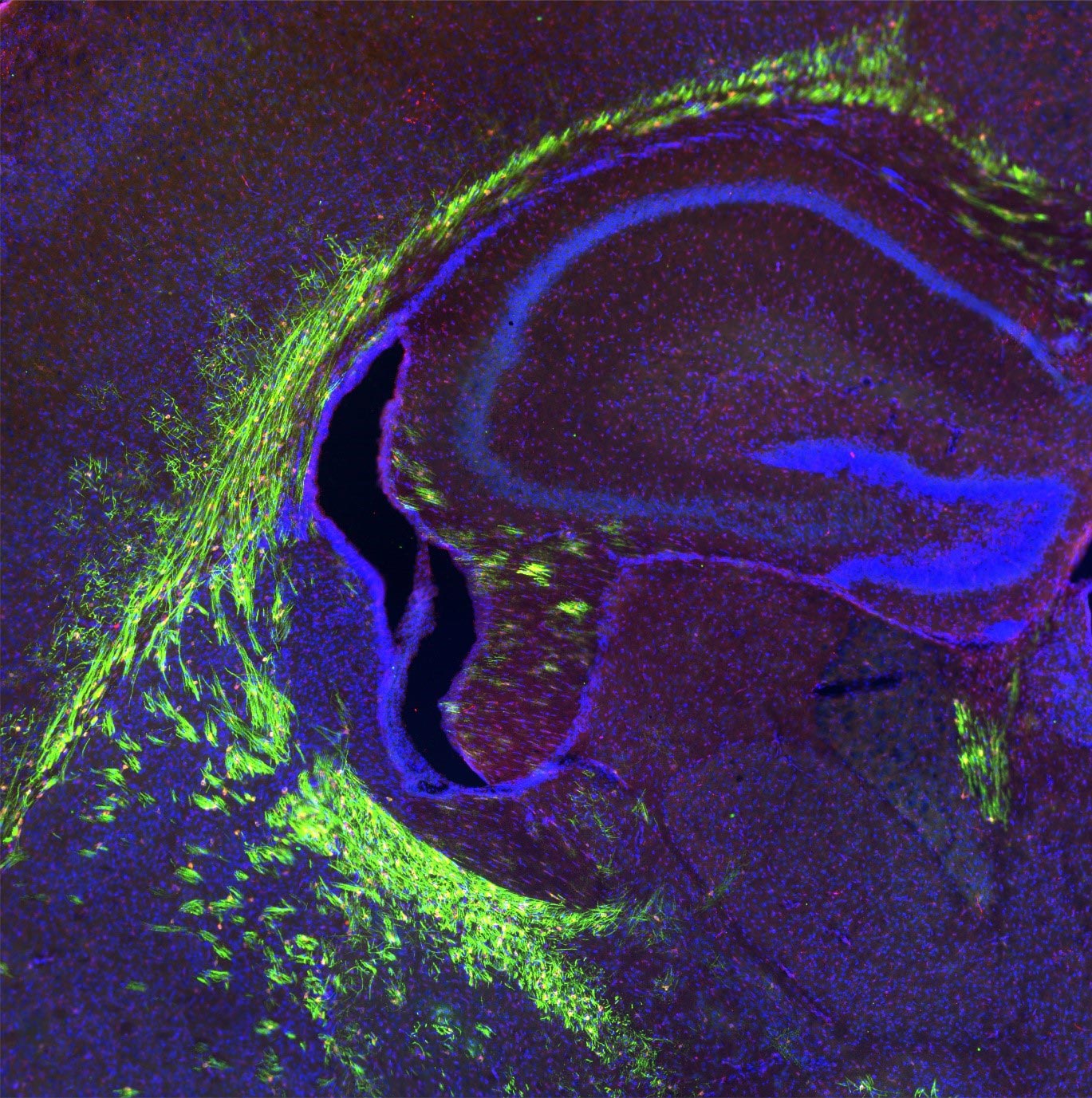
Cervello del modello preclinico in via di sviluppo con assoni mielinizzati (mostrato in verde). Scienziati di Singapore hanno scoperto il ruolo fondamentale della proteina trasportatrice Mfsd2a nella regolazione delle cellule cerebrali che mantengono le guaine mieliniche, la membrana isolante che avvolge i nervi. Questi risultati pubblicati in Giornale di indagine clinicaPuò aiutare a ridurre gli effetti dell’invecchiamento sul cervello. Mfsd2a trasporta la lisofosfatidilcolina (LPC), un lipide contenente acidi grassi omega-3, al cervello per la mielogenesi. Credito: Dott. Vetrivel Sengotuvil
I ricercatori hanno scoperto che la proteina trasportatrice Mfsd2a è essenziale per regolare le cellule cerebrali che mantengono le guaine mieliniche che proteggono i nervi. Questa scoperta potrebbe aiutare a ridurre gli effetti dell’invecchiamento sul cervello e portare a trattamenti per i disturbi neurologici causati dalla ridotta mielogenesi.
Scienziati di Singapore hanno mostrato il ruolo cruciale che una speciale proteina trasportatrice svolge nella regolazione delle cellule cerebrali che assicurano che i nervi siano protetti da coperture chiamate guaine mieliniche. I risultati, pubblicati dai ricercatori della Duke-NUS Medical School e della National University of Singapore nel Giornale di indagine clinicaPuò aiutare a ridurre gli effetti dannosi dell’invecchiamento sul cervello.
Una membrana isolante che circonda i nervi, le guaine mieliniche facilitano la conduzione rapida ed efficiente dei segnali elettrici in tutto il sistema nervoso del corpo. Quando la guaina mielinica è danneggiata, i nervi possono perdere la loro capacità di funzionare e causare disturbi neurologici. Con l’età, le guaine mieliniche possono naturalmente iniziare a deteriorarsi, motivo per cui le persone anziane perdono le loro capacità fisiche e mentali.
La perdita delle guaine mieliniche si verifica durante il normale processo di invecchiamento e nelle malattie neurodegenerative, come la sclerosi multipla e[{” attribute=””>Alzheimer’s disease,” said Dr. Sengottuvel Vetrivel, Senior Research Fellow with Duke-NUS’ Cardiovascular & Metabolic Disorders (CVMD) Program and lead investigator of the study. “Developing therapies to improve myelination—the formation of the myelin sheath—in aging and disease is of great importance to ease any difficulties caused by declining myelination.”
To pave the way for developing such therapies, the researchers sought to understand the role of Mfsd2a, a protein that transports lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC)—a lipid that contains an omega-3 fatty acid—into the brain as part of the myelination process. From what is known, genetic defects in the Mfsd2a gene leads to significantly reduced myelination and a birth defect called microcephaly, which causes the baby’s head to be much smaller than it should be.

Dr. Sengottuvel Vetrivel (left) and Prof David Silver (right). Credit: Duke-NUS Medical School
In preclinical models, the team showed that removing Mfsd2a from precursor cells that mature into myelin-producing cells—known as oligodendrocytes—in the brain led to deficient myelination after birth. Further investigations, including single-cell RNA sequencing, demonstrated that Mfsd2a’s absence caused the pool of fatty acid molecules—particularly omega-3 fats—to be reduced in the precursor cells, preventing these cells from maturing into oligodendrocytes that produce myelin.
“Our study indicates that LPC omega-3 lipids act as factors within the brain to direct oligodendrocyte development, a process that is critical for brain myelination,” explained Professor David Silver, the senior author of the study and Deputy Director of the CVMD Program. “This opens up potential avenues to develop therapies and dietary supplements based on LPC omega-3 lipids that might help retain myelin in the aging brain—and possibly to treat patients with neurological disorders stemming from reduced myelination.”
Previously, Prof Silver and his lab discovered Mfsd2a and worked closely with other teams to determine the function of LPC lipids in the brain and other organs. The current research provides further insights into the importance of lipid transport for oligodendrocyte precursor cell development.
“We’re now aiming to conduct preclinical studies to determine if dietary LPC omega-3 can help to re-myelinate damaged axons in the brain,” added Prof Silver. “Our hope is that supplements containing these fats can help to maintain—or even improve—brain myelination and cognitive function during aging.”
“Prof Silver has been relentless in investigating the far-reaching role of Msdf2a ever since he discovered this important lipid transport protein, alluding to the many possible ways of treating not only the aging brain but also other organs in which the protein plays a role,” said Professor Patrick Casey, Senior-Vice Dean for Research. “It’s exciting to watch Prof Silver and his team shape our understanding of the roles that these specialized lipids play through their many discoveries.”
Reference: “Deficiency in the omega-3 lysolipid transporter Mfsd2a leads to aberrant oligodendrocyte lineage development and hypomyelination” by Vetrivel Sengottuvel, Monalisa Hota, Jeongah Oh, Dwight L. Galam, Bernice H. Wong, Markus R. Wenk, Sujoy Ghosh, Federico Torta and David L. Silver, 27 April 2023, The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
DOI: 10.1172/JCI164118

“Sottilmente affascinante social mediaholic. Pioniere della musica. Amante di Twitter. Ninja zombie. Nerd del caffè.”





More Stories
Un decesso per il virus del Nilo occidentale è stato segnalato nella contea di Santa Clara – NBC Bay Area
Ultime notizie sugli astronauti della NASA: aggiornamento sull’equipaggio del Boeing Starliner bloccato nello spazio
Ci sono oceani sotto la superficie di Marte? La sonda InSight della NASA rivela un enorme serbatoio di acqua liquida